ERP Solutions
Are you running your company blind?
Get the insights
you need
when you need them.
What is ERP ?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a powerful software solution that enables businesses to streamline and manage their core processes—ranging from supply chain and manufacturing to financials and services. ERP systems drive operational efficiency by automating and integrating essential functions such as accounting, procurement, project management, customer relationship management, risk management, compliance, and supply chain operations. By consolidating these activities into a single, unified platform, ERP empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, enhance productivity, and maintain a competitive edge.
How Does an ERP System Work?
An ERP system works by integrating various core business functions into a single, unified system that provides real-time data and streamlines processes across departments. Here’s a breakdown of how an ERP system operates:
Database
for Business Functions
Processes
and Reporting
Collaboration
and Access Control
and Customization
External Systems
Centralized Database
Integrated Modules for Business Functions
Automated Processes
Real-Time Data and Reporting
Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Data Security and Access Control
Scalability and Customization
Integration with External Systems
Centralized Database
Core of ERP: An ERP system relies on a centralized database that stores information from various departments, such as finance, HR, sales, procurement, inventory, and more.
Single Source of Truth: This central database ensures that all departments have access to consistent, up-to-date information, reducing data silos and discrepancies.
Integrated Modules for Business Functions
Modular Structure: ERP systems are modular, with each module focusing on a specific business function (e.g., accounting, inventory, CRM). Businesses can select and configure modules according to their needs.
Interconnected Workflows: These modules are interconnected, meaning that information flows seamlessly between functions. For example, a sales order automatically updates inventory levels and triggers invoicing in accounting.
Automated Processes
Standardization and Automation: ERP systems standardize and automate repetitive tasks, such as order processing, billing, inventory management, and payroll. This reduces manual errors and speeds up workflows.
Workflow Management: Automated workflows guide tasks through predefined steps, ensuring they’re completed in the correct order. For instance, an order workflow might start with customer order entry, move to inventory check, then shipping, and finally invoicing.
Real-Time Data and Reporting
Immediate Updates: Changes made in one area of the ERP system are reflected across all relevant modules in real time. For example, when a product is shipped, inventory is immediately adjusted, and finance is updated for revenue reporting.
Data Analytics: ERP systems include built-in reporting and analytics tools that provide insights into performance metrics like sales, inventory turnover, and cash flow. This data helps decision-makers understand trends, track KPIs, and make informed decisions.
Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Enhanced Communication: By integrating various departments into one system, ERP fosters better collaboration. Team members from different functions can easily access the data they need and coordinate with other departments.
Improved Visibility: Managers and staff can see interdepartmental activities, making it easier to collaborate on projects, track orders, and align goals.
Data Security and Access Control
Role-Based Access: ERP systems offer role-based access control, ensuring that employees can only access the data relevant to their job functions.
Data Integrity and Security: Sensitive information is protected through data encryption, user authentication, and auditing capabilities, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Scalability and Customization
Flexible and Scalable: ERP systems are designed to scale with a business, allowing it to add users, modules, or features as the company grows.
Customization Options: ERP solutions can often be customized to fit specific workflows, industry needs, or regulatory requirements, ensuring that the system aligns with unique business processes.
Integration with External Systems
APIs and Third-Party Integrations: ERP systems can integrate with other applications, such as CRM tools, e-commerce platforms, and specialized software, through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
Seamless Data Flow: Integrations enable data to flow between the ERP and external systems, reducing the need for manual data entry and keeping information up-to-date across platforms.
Example of How ERP Works in Practice
Let’s consider a practical example of an ERP system at work in a retail company:
Sales Order
A customer places an order through the company’s website. The ERP system’s sales module records the order.
Inventory Check
The system automatically checks inventory to see if the items are available. If the items are in stock, the ERP updates the inventory count.
Warehouse Fulfillment
The warehouse team receives a notification in the ERP to pick, pack, and ship the order.
Shipping and Tracking
Shipping details are recorded, and the customer receives tracking information.
Invoicing and Accounting
The ERP automatically generates an invoice, sends it to the customer, and updates accounts receivable.
Reporting
Sales data is updated in real-time, and the finance team can monitor revenue and profit margins.
Benefits of an ERP System
Efficiency
By automating processes, ERP systems reduce manual work and streamline workflows.
Improved Decision-Making
Real-time data and analytics empower leaders to make informed, timely decisions.
Cost Savings
ERP systems help eliminate redundancies, optimize inventory, and reduce operational costs.
Enhanced Collaboration
ERP provides visibility across departments, encouraging better communication and teamwork.
In summary, an ERP system operates as the backbone of a business, connecting departments, automating tasks, and providing a unified view of operations. This integration and automation help companies improve productivity, reduce errors, and make data-driven decisions.
Selecting the best ERP
and the capabilities of different ERP solutions. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right ERP system:
1. Define Your Business Requirements
Set Goals: Outline what you hope to achieve with an ERP system, such as improved data accuracy, streamlined processes, real-time reporting, or support for growth.
List Specific Requirements: Make a list of must-have features and functions tailored to your business needs. This might include multi-currency support, specific compliance needs, or integration with other systems you use.
2. Involve Key Stakeholders
Gather Input: Involve representatives from different departments (e.g., finance, sales, operations, HR) to ensure the ERP system addresses each department’s needs.
Assign a Project Team: Designate a project team to lead the ERP selection process. They can evaluate options and coordinate feedback from each department.
3. Consider Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
Many ERPs are designed for specific industries, such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, or services. Industry-specific ERPs come with tailored features that can save you time on customization.
Research which ERP systems are popular and effective in your industry.
4. Evaluate ERP Functionalitye Data and Reporting
Core Functionality: Ensure the ERP covers all essential functions, such as finance, inventory, customer relationship management (CRM), and HR.
Advanced Features: Look for additional features that align with your business goals, such as AI-driven analytics, automation, and mobile accessibility.
Scalability: Choose an ERP system that can grow with your business, allowing you to add users, modules, or features as needed.


5. Assess Integration Capabilities
Compatibility with Existing Systems: If you already use software for CRM, e-commerce, or payroll, ensure the ERP can integrate with these systems.
API Availability: A flexible ERP should have APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow for easy data exchange and integration with third-party applications.
6. Consider Cloud vs. On-Premises Deployment
Cloud ERP: Offers flexibility, scalability, and remote access, making it ideal for businesses with distributed teams. It also reduces the need for on-site IT maintenance.
On-Premises ERP: Offers more control over data and customization but requires more IT infrastructure and resources for maintenance.
Hybrid Options: Some ERPs offer hybrid models, allowing you to store certain data on-premises while using cloud features.
7. Evaluate User Experience and Ease of Use
Interface and Usability: Choose a system that’s easy to use and intuitive, reducing the learning curve for your team.
Mobile Access: If your team needs access on the go, ensure the ERP system has a mobile-friendly interface or a dedicated mobile app.
8. Check Vendor Reputation and Support
Vendor Track Record: Research the vendor’s reputation, customer reviews, and industry experience.
Customer Support: Ensure the ERP provider offers reliable support, including implementation assistance, ongoing support, and training resources.
Community and Resources: Some ERPs have robust communities and knowledge bases, which can be helpful for troubleshooting and best practices.
9. Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Initial Costs: Consider the upfront cost of the software, hardware (if on-premises), and implementation.
Ongoing Costs: Factor in subscription fees (for cloud ERP), maintenance, upgrades, training, and support.
ROI: Evaluate how the ERP system will deliver a return on investment by improving efficiency, reducing costs, or increasing revenue.
10. Request a Demo and Trial Period
Ask for a Demo: Request live demos of shortlisted ERP systems to see how they handle specific business scenarios.
Trial Period: If possible, arrange a trial period to test the system with real data and workflows. This will give you hands-on experience and help you gauge user acceptance.
11. Read Reviews and Case Studies
User Reviews: Check reviews on websites like G2, Capterra, and Gartner to see what other businesses in your industry think of each ERP.
Case Studies and References: Ask vendors for case studies or customer references that demonstrate how their ERP system has benefited companies like yours.
12. Make a Final Decision
Use a scoring system to rank ERP solutions based on functionality, ease of use, cost, support, and other criteria.
Consider feedback from all stakeholders to make a well-rounded decision.

What is ERP Implementation?
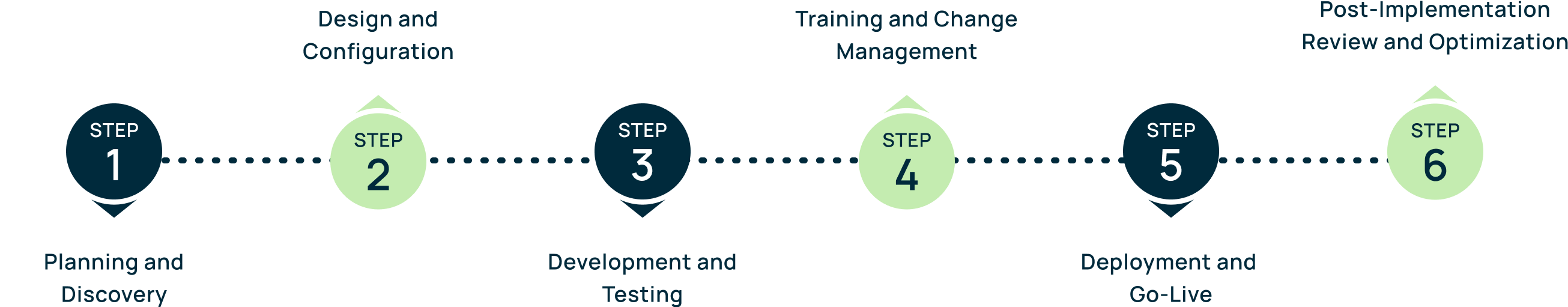
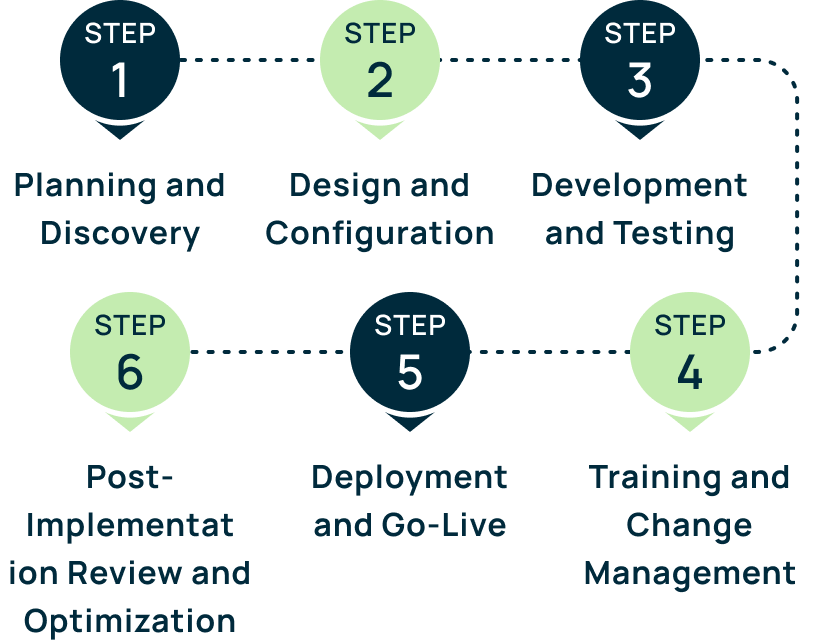
The ERP solution you need
We recognise that every business has distinct needs influenced by factors like industry, size, and market dynamics. That’s precisely why we provide customised solutions that can be finely adjusted to meet your specific requirements. Our dedicated team is committed to maximising the potential of your ERP platform, ensuring that you derive the utmost value from it. If you’re eager to discover how Jcurve can enhance your business operations, we encourage you to get in touch with us today. We’re here to assist you every step of the way.
Our consultants are here for you
Don’t know where to start on your ERP journey? Don’t worry; we can help. Our team of advisors can help you re-engineer and streamline your business, so it becomes even more productive. We bring people, technology and processes into one unified solution – and we help remove unproductive processes in the company. When you enlist Jcurve, our consultants will help you assess your current operating model and recommend improvements and solutions that work for you. We look at everything from workflows to information architecture and then recommend the most practical way forward to a better model. Our goal is always to find a way for you to improve your business and remain prepared for whatever the future may bring, and help your business reach its full potential.
Let’s get started today!
Let Jcurve propel your ambitions and unleash the full potential of your business with our powerful ERP solutions, meticulously tailored to optimise your business operations and drive profitability.
Contact our team now to discover how Jcurve ERP and Oracle NetSuite can empower the growth of your business while aligning seamlessly with your strategic objectives.
Let’s get started today!
Let Jcurve propel your ambitions and unleash the full potential of your business with our powerful ERP solutions, meticulously tailored to optimise your business operations and drive profitability.
Contact our team now to discover how Jcurve ERP and Oracle NetSuite can empower the growth of your business while aligning seamlessly with your strategic objectives.
Award-winning provider of Cloud ERP solutions successfully deployed by over 1000 clients across Australia, New Zealand and the Asia Pacific
Our cloud-based solutions, powered by Oracle NetSuite, offer an ERP platform suitable for businesses of all sizes operating in the Australian market.
Streamline Your Business Operations with an All-in-One ERP Platform
Our goal is to unify your business data into one always up-to-date application, allowing your team to make informed decisions quickly, aligned with Australian business requirements.

Our Solutions

Oracle NetSuite
Jcurve offers NetSuite ERP, a cloud-based software platform that enables businesses to manage various operations such as financials, customer relationship management, supply chain management, and more.

Jcurve ERP
Jcurve ERP is a cloud-based ERP solution designed to meet the needs of small and medium-sized enterprises in Australia. It provides a unified platform for managing business operations and processes, including financials, inventory, sales, and purchasing, tailored to business practices.

At Jcurve we build partnerships that help people and businesses grow. We aspire to be the leader in connecting you with your growth ambitions. Please leave your details and we will connect with you to understand how we can best help you with your growth journey.

The ‘Contact Me’ form is reserved for business inquiries. For career opportunities, please visit our Careers page.




