Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) are pivotal systems for modern businesses. ERP systems streamline and integrate internal business processes such as inventory management, finance, and human resources. On the other hand, CRM systems focus on managing customer interactions, enhancing sales, and optimizing marketing strategies. This article will explore the differences between ERP and CRM, their respective benefits, and how to choose the right system for your business needs.
Key Takeaways
- ERP focuses on integrating internal business processes.
- CRM centers on managing customer interactions.
- Both systems offer unique advantages depending on business needs.
What is ERP?

ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a comprehensive software system designed to integrate and manage core business processes across an entire organization. It acts as a central hub for data and processes, enabling different departments to work cohesively and efficiently. ERP systems are particularly beneficial for medium to large enterprises with complex operations, but smaller businesses with growth plans can also benefit from scaled-down ERP solutions. Popular ERP systems include: SAP ERP, Oracle ERP Cloud and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
Key aspects of ERP systems include:
- Integration: ERP unifies various business functions such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain management, and procurement into a single system.
- Real-time data: It provides real-time access to data across departments, improving decision-making and reducing data silos.
- Automation: ERP automates many routine tasks, reducing manual work and the potential for human error.
- Reporting and analytics: ERP systems often include robust reporting tools for in-depth analysis of business performance.
- Scalability: They are designed to grow with the business, accommodating increased data and users as the company expands.
- Modules: ERP systems are typically modular, allowing businesses to implement only the components they need.
What is CRM?

CRM, or Customer Relationship Management, is a strategy and supporting technology designed to manage and improve a company’s relationships and interactions with customers and potential customers. It focuses on customer retention and driving sales growth. Popular CRM systems include: Salesforce, HubSpot CRM and Zoho CRM.
Key aspects of CRM systems include:
- Customer-centric: CRM systems are designed to capture and analyze customer data to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Sales management: They help track the sales process from lead generation to closing deals.
- Marketing automation: CRM systems often include tools for creating, managing, and analyzing marketing campaigns.
- Customer service: They provide tools for managing customer inquiries, complaints, and support tickets.
- Analytics: CRM systems offer insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends.
- Collaboration: They facilitate better communication between sales, marketing, and customer service teams.
Benefits of ERP Systems
ERP systems offer several advantages:
- Streamlining internal processes: By integrating various business functions, ERP systems reduce redundancies and improve efficiency.
- Reducing operational costs: Automated processes and improved resource management lead to cost savings.
Benefits of CRM Systems
CRM systems provide unique benefits:
- Improving customer satisfaction and loyalty: Personalized interactions and responsive customer service enhance customer relationships.
- Enhancing sales and marketing strategies: CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior, enabling targeted marketing and sales efforts.
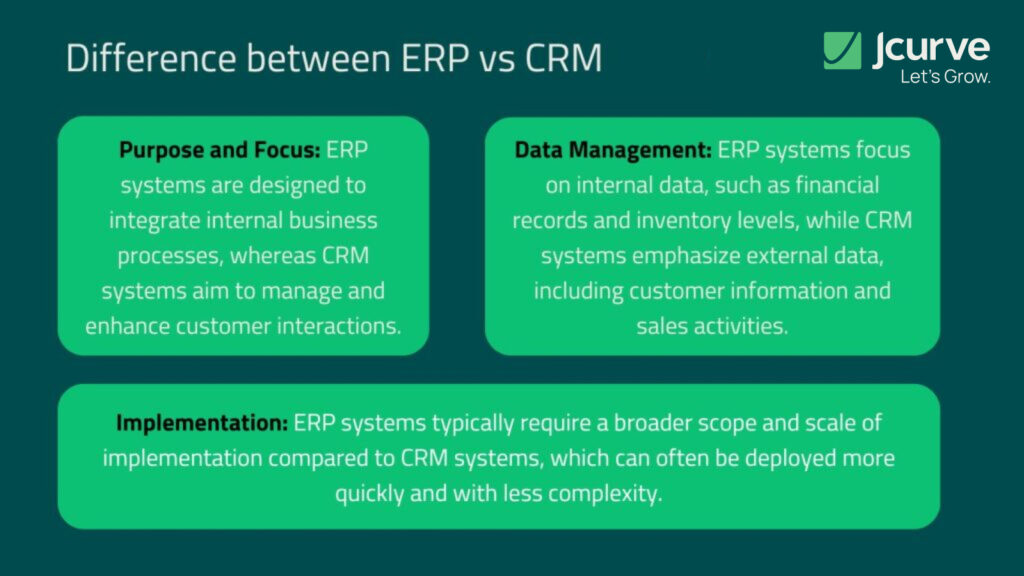
ERP vs CRM: Key Differences
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems serve distinct but complementary roles in business management. ERP systems focus on streamlining internal processes by integrating core business functions—including finance, supply chain, human resources, and manufacturing—into a unified system. This integration enhances process efficiency, reduces redundancies, and fosters real-time data access for informed decision-making.
Conversely, CRM systems are designed to enhance customer relationships and improve sales strategies. By managing customer data, tracking interactions, and analyzing customer behaviors, CRM systems enable businesses to tailor their marketing efforts and improve service delivery.
How ERP and CRM Work Together?
Integrating ERP and CRM systems can provide numerous benefits, such as enhanced data flow and improved decision-making capabilities. This integration facilitates streamlined processes by ensuring that information flows seamlessly between departments, reducing the chances of data silos.
Enhanced data accuracy is another benefit; synchronized systems allow for real-time updates, minimizing errors that can occur when using disparate systems. For instance, retail giants like Amazon leverage integrated systems to provide timely support, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Moreover, informed decision-making is significantly enhanced. Access to consolidated data allows businesses to analyze trends and performance metrics, leading to strategic insights. In manufacturing, companies like Siemens utilize this integration to optimize production schedules based on customer demand.
ERP vs CRM: Which is Better for Your Business?
Organizations often grapple with the choice between implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system and a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) solution, both of which serve critical yet distinct functions. Choosing between ERP and CRM depends on several factors:
- Business size and industry: Larger businesses with complex operations may benefit more from ERP systems, while smaller companies or those focused heavily on customer interactions might find CRM systems more advantageous.
- Specific needs: Assessing the unique requirements of your business can help determine which system aligns best with your goals. You can ask us on how to implement the system into your business.
- Cost implications and ROI comparison: Evaluating the total cost of ownership and potential return on investment is crucial in making an informed decision.
How to Choose the Right System
Define Budget and ROI Expectations: Determine your investment capacity, considering both upfront and long-term costs. Factor in the potential return on investment for each system type.





